This week in toast, AI knows how you feel, Mars turns out to be quite lively, and robots learn to touch you in ways that aren't alarming. Meanwhile, scientists have confirmed cold water immersion is actually good for you, vindicating masochists worldwide.
🤖 AI Therapists Are Better Than Most Humans
Researchers at Dartmouth have conducted the first clinical trial of an AI-powered therapy chatbot and found that people with diagnosed mental disorders experienced significant improvements in their symptoms over eight weeks. Users engaging with "Therabot" reported their interactions were comparable to working with actual human therapists. Depression symptoms were down 51%, anxiety down 31%, and eating disorder concerns down 19%.
🧐 What's in it for me? There’s a startling therapist shortage across most developed countries, so this research is welcome news. The AI delivered results "comparable to gold-standard cognitive therapy with outpatient providers," according to researchers. Given that NHS waiting lists are measured in geological eras rather than weeks, this could massively improve access to therapeutic support for those most in need. The researchers do note that clinician oversight remains critical, so your therapist's job is safe for now.
💵 Out of the Lab: Mental health tech startups will be delighted with these findings. Companies like Woebot Health have already raised significant funding for AI-powered mental health platforms, while Wysa (Series B) continues to expand its AI therapy services globally. The digital mental health market is projected to reach £37 billion by 2027, with firms racing to blend human oversight with AI accessibility. Meanwhile, established providers like Calm and Headspace are likely examining how to integrate similar conversational AI capabilities into their existing platforms.
👋 Next Generation Haptics Have Arrived
Northwestern University researchers have developed a groundbreaking haptic device that goes beyond simple vibrations to deliver realistic touch sensations. This compact, lightweight, wireless device applies force in any direction to generate a variety of sensations, including vibrations, stretching, pressure, sliding, and twisting. Unlike most current haptic technologies that merely "poke" at the skin, this device engages all mechanoreceptors in the skin, both individually and in combination.
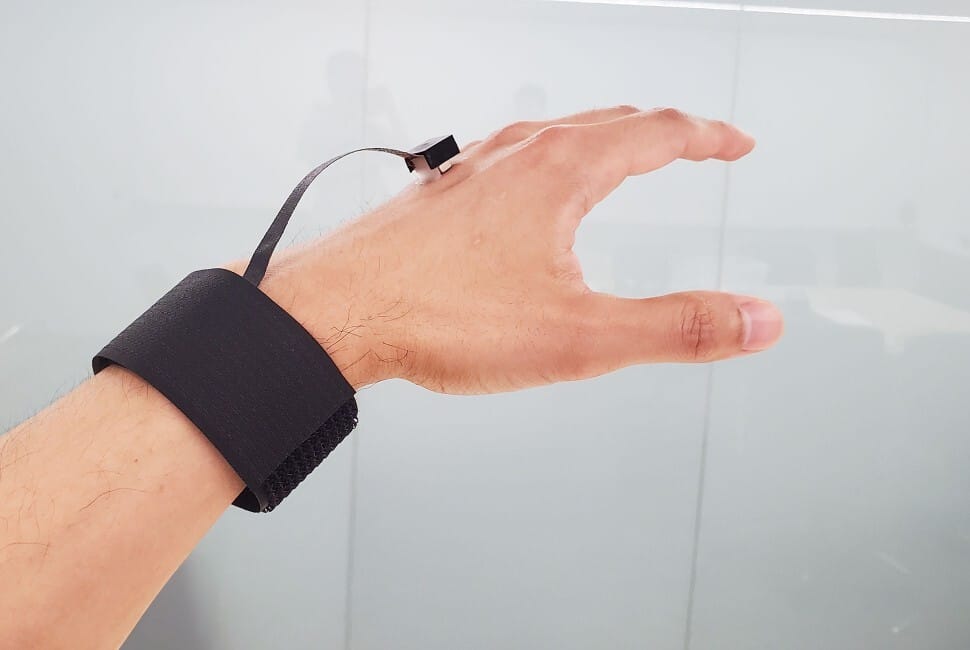

🧐 What's in it for me? While visual and audio technologies have advanced rapidly, haptic feedback has remained stubbornly basic. This new approach could revolutionise virtual reality experiences by making them feel as realistic as they look. Imagine shopping online and feeling the texture of fabrics or playing games with sensations beyond simple controller rumbles. The researchers even demonstrated converting music into physical touch, allowing users to feel different instruments through varying vibration patterns.
💵 Out of the Lab: The haptic technology market is projected to reach £28 billion by 2026, with several companies poised to implement these advances. HaptX (Series B) has already developed gloves providing detailed haptic feedback for virtual reality. Ultraleap (formerly Ultrahaptics) continues to advance mid-air haptic technology for touchless interfaces. Meanwhile, bHaptics (Series C) creates wearable haptic products for VR/AR applications. Even established players like Meta are investing heavily in haptic research for their metaverse ambitions. The first companies to integrate this multi-directional force technology into consumer products could literally touch consumers in ways their competitors can't, which sounds slightly less creepy in context…
🧠 Your Mind's New USB Port
Researchers have developed a revolutionary memristor-based brain-computer interface (BCI) that can effectively co-evolve with changing brain signals. This innovative approach implements energy-efficient adaptive neuromorphic decoders that maintain stable performance as your brain does what brains do best: constantly change. In real-world testing, the system achieved 85.17% decoding accuracy in drone flight control tasks while consuming 1,643 times less energy than conventional systems.
This is a little complicated so let's break it down:
Memristors are electrical components that "remember" the amount of charge that flowed through them
Neuromorphic decoders are circuits designed to mimic how neurons process information
This system creates a feedback loop where both the brain and the machine adapt to each other
Traditional BCIs need constant recalibration; this one adapts on its own
Result: 20% higher accuracy and dramatically lower power consumption

🧐 What's in it for me? Current BCIs struggle to maintain consistent performance because brain signals are about as stable as the cryptocurrency market. This new system actually adapts alongside your changing brain patterns, creating a co-evolution that yielded 20% higher accuracy in tests. For people with mobility impairments, this could mean more reliable control of assistive devices without constant recalibration.
💵 Out of the Lab: The BCI market is heating up with players like Neuralink and Synchron (Series C) developing implantable interfaces. Meanwhile, Paradromics (Series A) is working on high-data-rate neural interfaces that could benefit from this adaptive technology. The researchers are now collaborating with HKU Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine and Queen Mary Hospital to apply these advances to epilepsy analysis.
🧠 Artificial Neurons Learn to Organise Themselves
Researchers from the University of Göttingen and the Max Planck Institute have developed novel artificial neurons that learn independently and are more strongly modelled on their biological counterparts. These "infomorphic neurons" organise themselves amongst neighbouring neurons, deciding which inputs are relevant without external control. Inspired by pyramidal cells in the cerebral cortex, each neuron can be programmed to seek redundancy with neighbours, collaborate synergistically, or specialise in its own part of the network's information.

A Meerkat based representation of a Pyramidal Cell
🧐 What's in it for me? Current artificial neural networks require extensive oversight to learn effectively, making them powerful but inefficient energy hogs. These self-organising neurons could lead to AI systems that use significantly less power while adapting more flexibly to new information. This might mean future smartphones that learn your habits without draining your battery, or smart home systems that actually get smarter rather than just more annoying.
💵 Out of the Lab: This approach could revolutionise machine learning hardware development. Companies like SynSense (formerly aiCTX) are already working on neuromorphic computing chips that mimic brain function. BrainChip (publicly traded) offers commercial neuromorphic processors that could implement these self-organising algorithms. As energy efficiency becomes increasingly crucial in AI deployment, expect to see early adopters of this technology gaining significant advantages in mobile and embedded applications.
🔍 Tiny Rolling Robot Takes Virtual Biopsies, Saving You The Discomfort
Engineers from the University of Leeds have developed a tiny magnetic robot capable of taking high-resolution 3D ultrasound scans from deep inside the body. This miniature marvel, approximately the size of a 1p coin, uses an oloid shape (a little-known 3D form) to achieve previously impossible rolling motion essential for precise navigation and imaging inside the body. The team says this is the first time it's been possible to generate high-resolution three-dimensional ultrasound images from deep inside the gastrointestinal tract.

🧐 What's in it for me? Colorectal cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths globally, but if detected early, it's highly treatable. This rolling robot could transform diagnosis by enabling "virtual biopsies"—non-invasive scans providing immediate diagnostic data—allowing doctors to detect, stage, and potentially treat lesions in a single procedure. No more waiting anxiously for biopsy results or undergoing multiple unpleasant procedures. The magnetic approach is particularly clever, as magnetic fields pass harmlessly through human tissue while allowing precise control of the tiny robot. Good news for anyone who's ever dreaded a colonoscopy, which is essentially everyone who knows what a colonoscopy is.
💵 Out of the Lab: Medical robotics is an increasingly active field, with companies like Medtronic already investing in robotic surgical systems. The sector is seeing significant investment momentum, with CMR Surgical recently raising $200 million in debt and equity. The global medical robotics market is expected to exceed £20 billion by 2026, with diagnostic robots representing a significant growth segment. As healthcare systems worldwide struggle with cancer screening backlogs, technologies that enable faster, less invasive diagnostics could find rapid clinical adoption, potentially rolling into an examination room near you sooner than you might think.
👽 Martian Molecules Hint at Ancient Life Potential
Scientists have detected the longest organic molecules identified to date on Mars, containing up to 12 consecutive carbon atoms. These long carbon chains could exhibit features similar to the fatty acids produced by biological activity on Earth. Thanks to Mars's lack of geological activity and its cold, arid climate, this organic matter has been preserved in a clay-rich sample for approximately 3.7 billion years, dating from the same period during which life first emerged on Earth…
While this doesn't confirm life on Mars, it's certainly giving astrobiologists something to get excited about. These molecules date from an era when Mars was potentially more habitable, with liquid water on its surface.

🧐 What's in it for me? The finding is particularly significant because these complex organic molecules are similar to the building blocks of life as we know it. For space exploration enthusiasts, this discovery increases the possibility that we might eventually find evidence of ancient microbial life on the Red Planet.
💵 Out of the Lab: This discovery could influence future Mars exploration missions and potentially commercial space ventures. SpaceX continues to develop its Mars colonisation plans, while Astrobotic (Seed) is building technologies for lunar and planetary missions. The findings will particularly inform ESA's upcoming ExoMars mission launching in 2028 and the joint NASA-ESA Mars Sample Return mission planned for the 2030s. As our understanding of extraterrestrial organic chemistry improves, companies developing life-detection technologies and in-situ resource utilisation methods stand to benefit significantly, potentially answering the age-old question: are we alone? (Or at least, were we alone 3.7 billion years ago?)
🌀 Quantum Computers Get Self-Aware
Researchers from Tohoku University and St. Paul's School, London, have developed a new algorithm that allows quantum computers to analyse and protect their own quantum entanglement; a fundamental underpinning of quantum computing often characterised by Einstein as "spooky action at a distance." The team introduced a method called variational entanglement witness (VEW), using a quantum algorithm that optimises entanglement detection, enhancing accuracy while better differentiating between separable (not entangled) and entangled states.
Breaking it down, quantum entanglement is what gives quantum computers their extraordinary power, but it's also notoriously fragile and difficult to maintain. This new approach allows quantum systems to essentially monitor and protect their own foundational resources. It's somewhat like having your car perform its own diagnostics and repairs while you're driving it.

🧐 What's in it for me? For anyone interested in the practical applications of quantum computing, this could help accelerate the development of reliable quantum technologies for drug discovery, materials science, and complex optimisation problems. Quantum computers understanding themselves better means they'll eventually solve our problems better.
💵 Out of the Lab: The quantum computing landscape continues to evolve rapidly, with players like IBM Quantum and Rigetti Computing developing increasingly powerful quantum processors. Startups such as Q-CTRL (Series B) specialise in quantum control infrastructure software that could implement these self-analysis algorithms. Quantum Brilliance (Series A) is working on room-temperature diamond-based quantum computers that would particularly benefit from enhanced entanglement protection. As quantum computers scale up toward practical advantage, technologies that improve entanglement stability and detection could become critical competitive differentiators, helping ensure quantum computations give meaningful answers, like 42.
🍄 Separating the Magic from the Mushroom
Can we get the mental health benefits of psychedelics without having elephants show up in our living rooms? That's the question researchers tackled when investigating the role of the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor in psychedelics' antidepressant effects. Using a chronic despair mouse model, they tested two psychedelics (DOI and psilocybin) and a non-hallucinogenic 5-HT2A receptor agonist (lisuride). All three drugs induced anxiolytic (reduction in anxiety) and antidepressant-like effects lasting up to 15 days after a single injection.
The fascinating part? While DOI and lisuride needed the 5-HT2A receptor to work their mood-lifting magic, psilocybin remained effective even in mice lacking this receptor, hinting that there are other unknown mechanisms of action at work.
🧐 What's in it for me? The holy grail of depression treatment would be fast-acting, long-lasting relief without the kaleidoscopic side effects. This research suggests the hallucinogenic trip might not be necessary for the entire therapeutic benefit. Conventional antidepressants often take weeks (if not months) to work and leave about 30% of patients still struggling. Psychedelics, meanwhile, can produce rapid improvements lasting for weeks or more after just one dose. If pharmaceutical companies can isolate the mood-enhancing pathways while bypassing the hallucinations, we might soon see antidepressants that work in hours, with no need for a psychedelic guide or a carefully controlled setting.
💵 Out of the Lab: COMPASS Pathways is a leader in this space, running clinical trials of psilocybin therapy for treatment-resistant depression while investigating these mechanisms. Delix Therapeutics (Series A) is specifically developing non-hallucinogenic psychoplastogens; compounds that promote neural plasticity like psychedelics but without perceptual effects. Atai Life Sciences has a diverse portfolio including both hallucinogenic and non-hallucinogenic approaches. The race to develop the first non-hallucinogenic fast-acting antidepressant based on psychedelic mechanisms represents a potential multi-billion pound market opportunity.
IN OTHER NEWS
Researchers Discover AI Can't Replace… Researchers
In a spot of considerable luck for a group of University of Florida researchers, they have uncovered that they’re entirely irreplaceable. After putting ChatGPT, Microsoft's Copilot, and Google's Gemini through their academic paces, the team found these AI models were decent at brainstorming ideas and designing research methods but fell flat when it came to literature reviews, analyzing results, and writing complete manuscripts.
"A pervasive fear surrounding these AIs is their ability to usurp human labor," explained Geoff Tomaino, "In general, we found that these AIs can offer some assistance, but their value stops there, as assistance." That’s handy.
AND FINALLY…
Cold Plunges Actually Change Your Cells (In a Good Way) 🥶

For the Cells
Researchers at the University of Ottawa have finally provided scientific evidence for what ice bath enthusiasts have been claiming all along: cold water immersion significantly alters cellular function.
The study found that after seven consecutive days of one-hour cold water immersion at 14°C participants showed significantly improved autophagic function; the cellular "recycling system" that promotes health by removing damaged components. While the first cold exposure temporarily disrupted this cellular recycling process, repeated exposure over a week actually strengthened it, leading to more efficient cellular cleanup and reduced damage markers.
This enhanced cellular resilience could have important implications for health and longevity, potentially preventing the onset of various diseases. The researchers caution that these results apply specifically to the young males in the study, so more research is needed for other groups. Still, it provides some scientific backing for the cold water immersion trend that has everyone chattering 🙄.
Until next time, stay curious.
Like what you're reading? Share toast with a friend.